[10000ダウンロード済み√] yield stress on stress strain curve 112288-Yield stress from stress strain curve excel
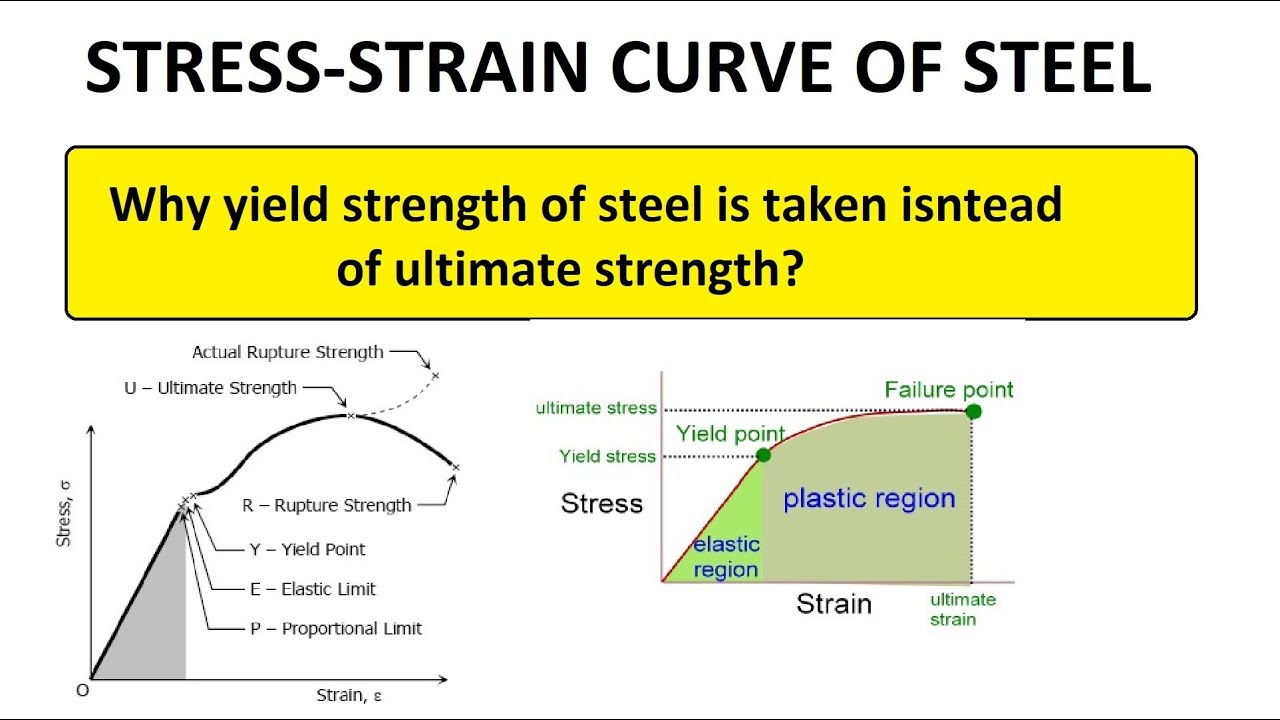
Shearing stress stress that tends to shear the material acts inStrain Hardening Strain Hardening occurs when a material experiences plastic deformation During this the yield point is permanently moved to the right on the stress strain curve which leads to increasing the yield stress or hardening of the materialTo manage problems related to yield stress, engineers and scientists rely on a variety of formulas dealing with the mechanical behavior of materials Ultimate stress, whether it is tension, compression, shearing or bending, is the highest amount of stress a material can withstand
Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
Yield stress from stress strain curve excel
Yield stress from stress strain curve excel-The stress–strain curve is produced by plotting the applied stress on the fibre axis and the elongation produced due it The stress–strain curve of a model fibre is shown in Fig 31 Different types of fibre produce different stress–strain curves The nature of each curve is profoundly influenced by the structure of the fibreYield Strength Graph Each and every material possess characteristic stressstrain curve that allows us to determine what application they are best suited for Each materials curve possesses different points of transition ie from elasticity to plasticity and finally to breakage



The Stress Strain Curve Obtained By Loading A Sample Of Compact Bone In Download Scientific Diagram
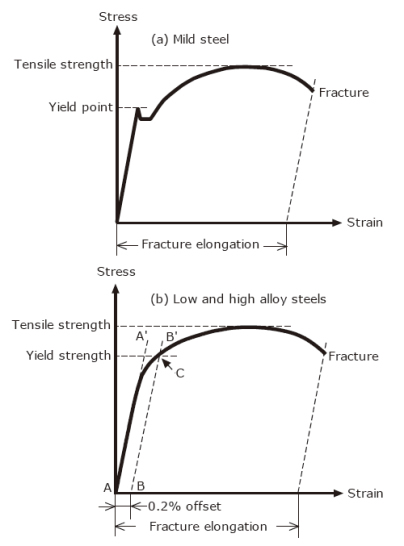
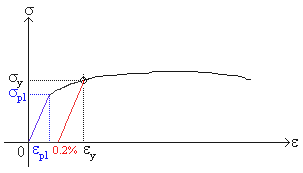
The plastic region is where if stress is released from the material it will retain permanent deformation and strain hardening Strain Hardening Strain Hardening occurs when a material experiences plastic deformation During this the yield point is permanently moved to the right on the stress strain curve which leads to increasing the yieldDraw a line parallel with the modulus slope with 02% offset, the stress/strength at the intersection with the graphs will be the 02% yield stress/strengthStress is the force per crosssectional area that a material withstands Strain is the percent change in the length of the material The stressstrain curve is the simplest way to describe the mechanical properties of the material
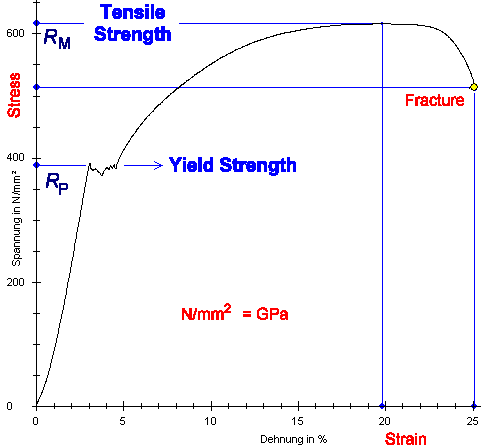
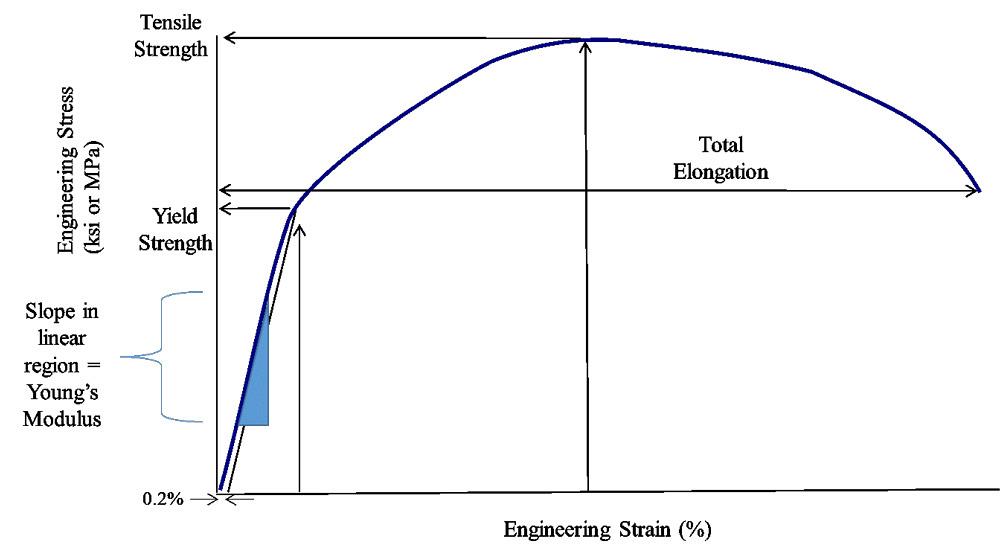
Applications that do not require impact strength or tolerance to heat loads *Toughness is not defined in ASTM D638 though can be calculated by taking the integral of the stressstrain curve collected by tensile dataYield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stressYield strengths range from 110 ksi through 140 ksi, but we can temper it to other strength levels When compared with standard 4140 heat treated to the same tensile and yield strengths, 4140HW achieves significantly higher toughness, as measured by impact strength (see Figure 9) 4140HW combines medium carbon content with highend chromium,
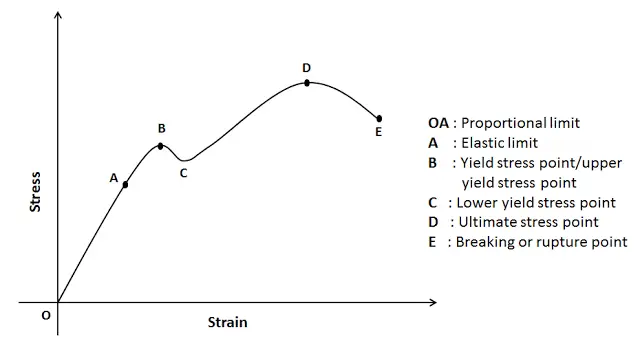
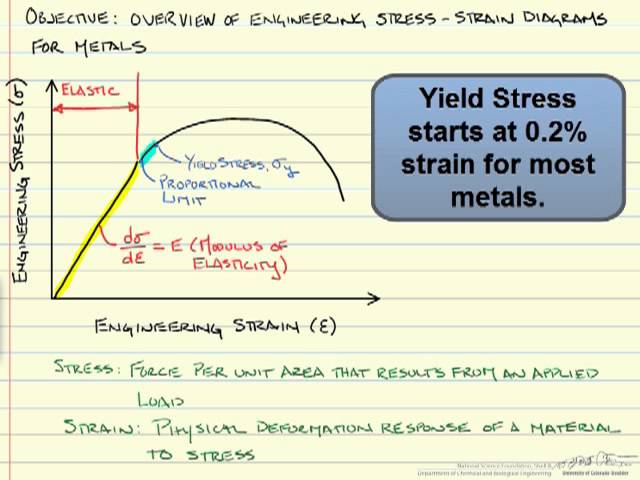
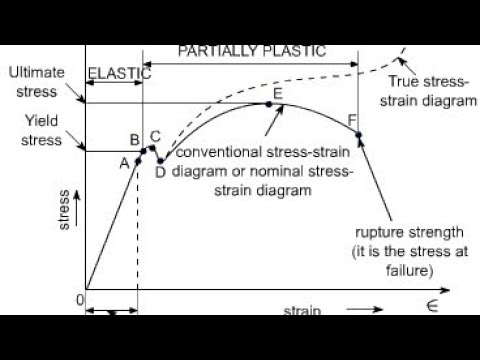
Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Questions on "Stress & Strain Curve" 1 The slope of the stressstrain curve in the elastic deformation region is _____ a) Elastic modulus b) Plastic modulus c) Poisson's ratio d) None of the mentioned Answer a Clarification The elastic modulus is the ratio of stress and strain So on the stressYield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axisYield Point or Yield Stress Point Yield point in a stress strain diagram is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically After the yield point is passed there is permanent deformation develops in the material and which is not reversible There are two yield points and it is upper yield point and lower yield point



Yield Strength Engineer Educators Com



Stress Strain Diagram Part 2
Hooke's Law and Stressstrain Curve The point B in the curve is the Yield Point or the elastic limit and the corresponding stress is the Yield Strength (S y) of the material Once the load is increased further, the stress starting exceeding the Yield Strength This means that the strain increases rapidly even for a small change in the stressIt is difficult to measure the yield strength of ceramics as they tend to fracture before they enter the plastic deformation region, ie, they are brittle as shown in the figure below StressStrain curves for two brittle materials Threepoint bending apparatus used determine stressstrain behaviorThis set of Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Stress & Strain Curve" 1 The slope of the stressstrain curve in the elastic deformation region is _____ a) Elastic modulus b) Plastic modulus c) Poisson's ratio d) None of the mentioned View Answer


Stress Strain Curve Explanation Stages Mild Steel Engineering Intro


Stress Strain Curve Relationship Diagram And Explanation Mechanical Booster
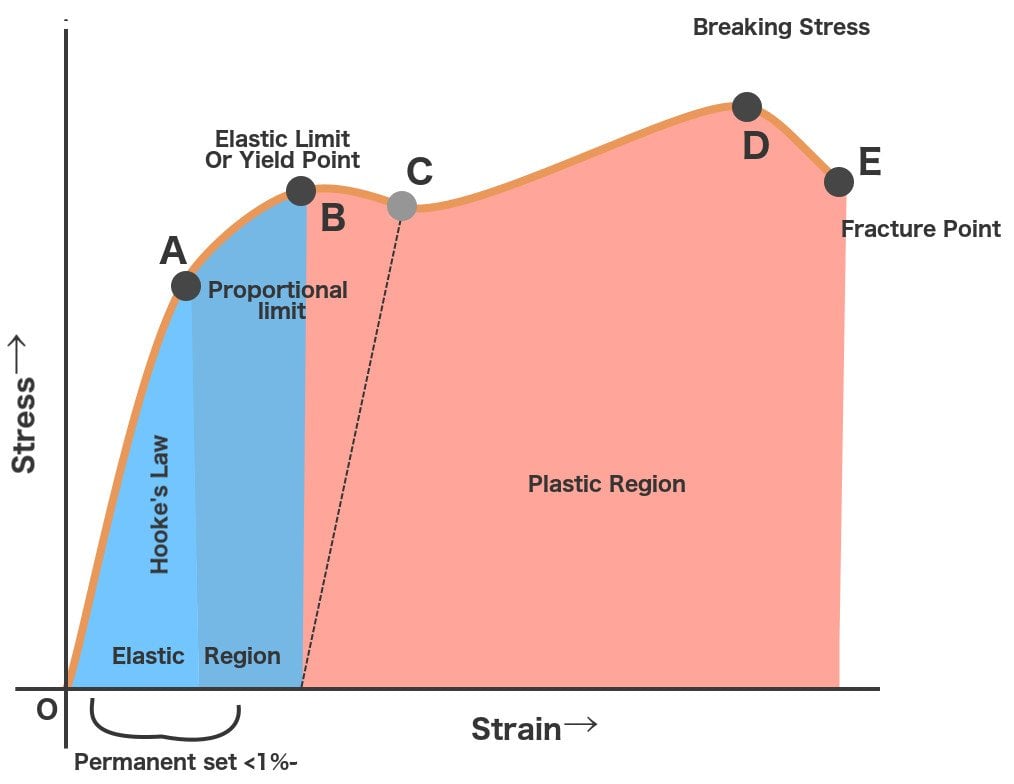
The stressstrain curve provides design engineers with a long list of important parameters needed for application design A stressstrain graph gives us many mechanical properties such as strength, toughness, elasticity, yield point, strain energy, resilience, and elongation during load It also helps in fabricationStretch can be observed on a Tensile StressStrain Diagram To the left is the stresselongation curve Steel possesses a certain amount of elasticity as it is stretched Thus, a bolt that is properly tensioned should be functioning in the elastic range (as viewed on the Diagram) If the load is removed andFracture or breaking point (i) Proportional Limit It is the region in the stressstrain curve that obeys Hooke's Law In this limit, the ratio of stress with strain gives us proportionality constant known



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



A Tensile Engineering Stress Strain Curve Of Matrix Sample B Download Scientific Diagram
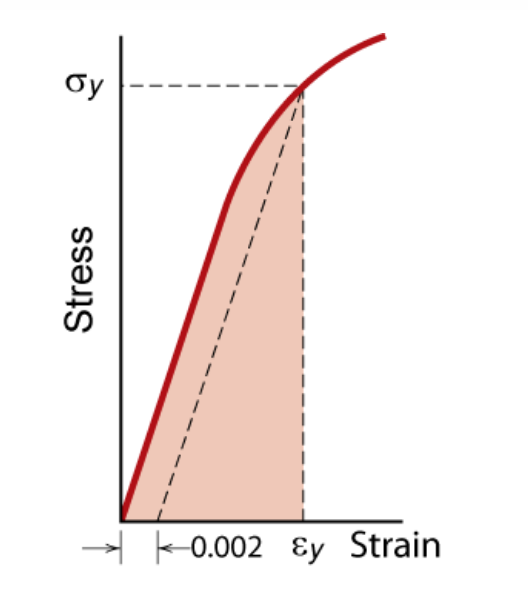
The yield point is not necessarily very clear, and it is generally obtained by an offset method Y is considered to be the intersection of an offset line, parallel to the linear portion of the stressstrain curve typically at 0002 axial strain, and the plastic portion of the curveApplications that do not require impact strength or tolerance to heat loads *Toughness is not defined in ASTM D638 though can be calculated by taking the integral of the stressstrain curve collected by tensile dataThe stressstrain curve and a straight line with slope of E and beginning at 0002 (02%) on the strain axis The most satisfactory definition of yield strength for aluminum alloys and many other materials Note At this definition of yield, the plastic portion of the strain is 0002 and the elastic portion of the strain is σ y σ σ y E E 1



What Is The Significance Of The Zig Zag Portion In A Stress Strain Curve Quora


Engineering Stress Strain Curve
The stressstrain graph has different points or regions as follows Proportional limit;The stressstrain curve and a straight line with slope of E and beginning at 0002 (02%) on the strain axis The most satisfactory definition of yield strength for aluminum alloys and many other materials Note At this definition of yield, the plastic portion of the strain is 0002 and the elastic portion of the strain is σ y σ σ y E E 1Compressive stress stress that tends to compress or shorten the material acts normal to the stressed area;



Yield Point Instron



The Stress Strain Curve Intro To Structural Engineering
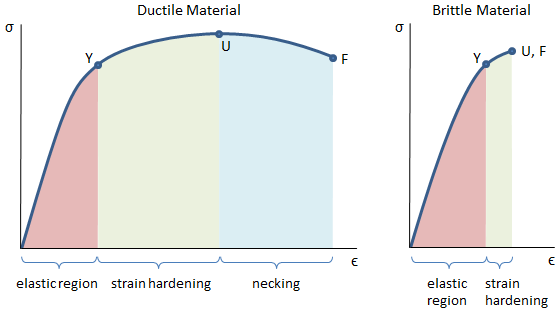
Brittle StressStrain Curve In the brittle material curve, a yield strength or yield point is the same as the fracture point The brittle material curve reveals that the material fractures orIn engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and strain can be determined (see tensile testing)Yield point The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange
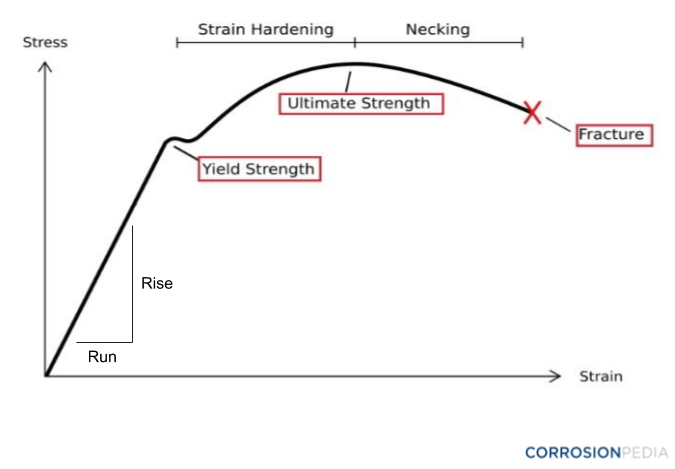
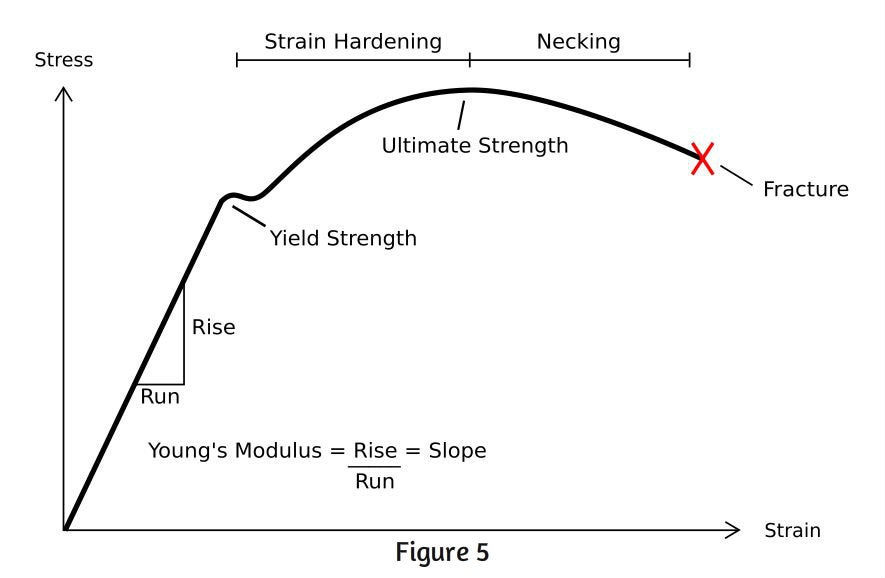
Yield stress and strength will now be sought Yield Stress Definition Consider a typical, ductile material stress strain curve as shown in Fig 1 Fig 1 Stress strain curve The related constitutive form will be taken to be that of the strain hardening type and applicable to any standard test such as those forBrittle StressStrain Curve In the brittle material curve, a yield strength or yield point is the same as the fracture point The brittle material curve reveals that the material fractures orOne of stages in the stressstrain curve is the strain hardening region This region starts as the strain goes beyond yield point, and ends at the ultimate strength point, which is the maximal stress shown in the stressstrain curve



Stress Strain Curves Of High Strength Steels With Approximately The Download Scientific Diagram



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital
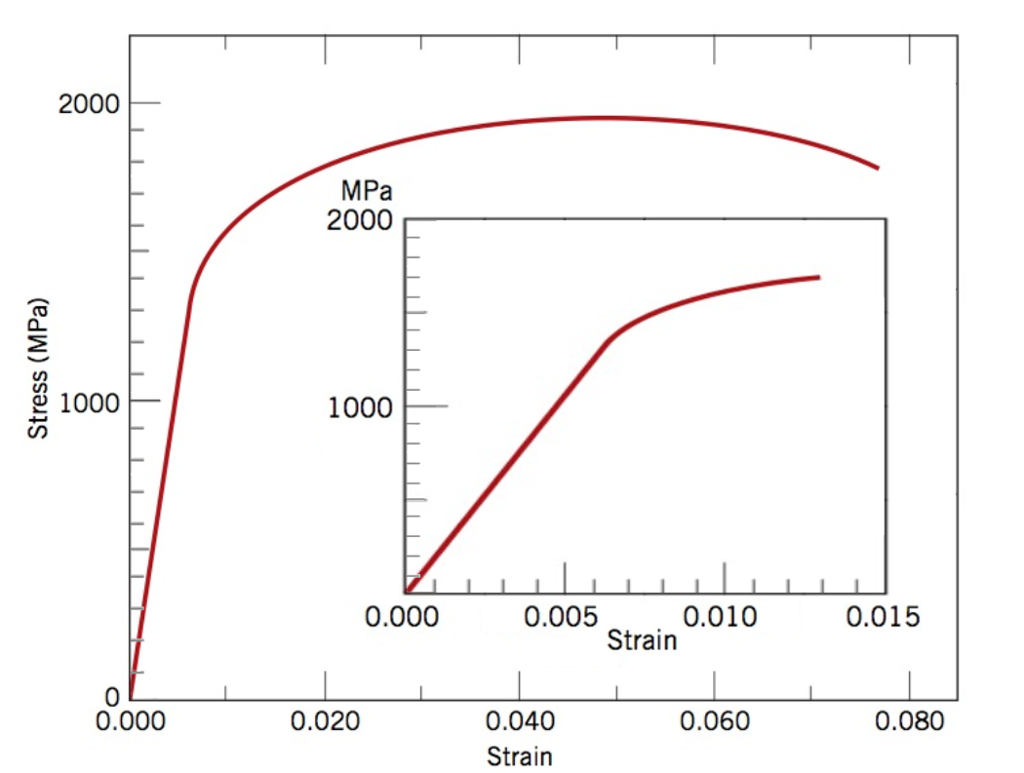
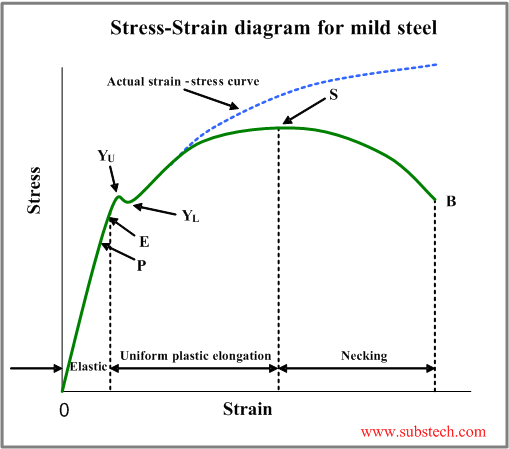
Where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based on the provided inputs Based on the specified material properties, the value of the strain hardening exponent, n, isAs shown in stress strain curve for mild steel, up to the point A, stress and strain follow a relationship This is known as Hook's law Up to the limit of proportionality, stress directly followed the strain This means ratio of stress and strain remains constantHigh mechanical strength and rigidity, without the need for fillers/reinforcements or other modifications Outstanding creep resistance and longterm fatigue endurance These features of high mechanical strength and toughness can be seen in this overlay of stressstrain curves of high viscosity Delrin ® acetal homopolymers and standard acetal
.jpg)


Determining And Understanding The Yield Stress Of Complex Fluids



Stress Strain Diagram Instron
This point is known as the yield point A further increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress The stressstrain behavior of a polymer greatly depends on the temperature At very low temperature well below the glass transition temperature, brittle failure is observed as a break at low strain rate at the stress maximumTo manage problems related to yield stress, engineers and scientists rely on a variety of formulas dealing with the mechanical behavior of materials Ultimate stress, whether it is tension, compression, shearing or bending, is the highest amount of stress a material can withstandThe stressstrain curve relates the applied stress Applied Stress The stress applied to a part or assembly as a result of external forces or loads to the resulting strain Strain A measure of relative change in the size or shape of a body



Explanation Of Stress Strain Curve


1
Yield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point (BC) is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point (D)In the stressstrain curve for the brittle material below, a very small region of strain hardening is shown between the yield point Y and the ultimate strength U Note however that a brittle material may not actually exhibit any yielding behavior or strain hardening at all in this case, the material would fail on the linear portion of the curveIn the stressstrain curve for the brittle material below, a very small region of strain hardening is shown between the yield point Y and the ultimate strength U Note however that a brittle material may not actually exhibit any yielding behavior or strain hardening at all in this case, the material would fail on the linear portion of the curve


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia


Engineering Stress And Strain Curve Diagram
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent andAs the stress increases, the strain caused by it varies according to the properties of a material The relationship can be limned by a graph, and this graph is referred to as the stressstrain curve, where stress is plotted on the Yaxis and strain is plotted on the XaxisStress stress diagram construction from test results, finding elastic modulus, yield strength, tensile strength, ductility, resilience and toughness as exact


Science Of Uniaxial Deformation


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation
Yield strengths range from 110 ksi through 140 ksi, but we can temper it to other strength levels When compared with standard 4140 heat treated to the same tensile and yield strengths, 4140HW achieves significantly higher toughness, as measured by impact strength (see Figure 9) 4140HW combines medium carbon content with highend chromium,Yield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point (BC) is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point (D)The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior



Strength At Break Tensile



Are Safety Point And Yield Point The Same In A Stress Strain Diagram Quora
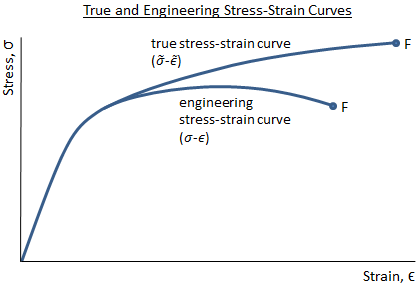
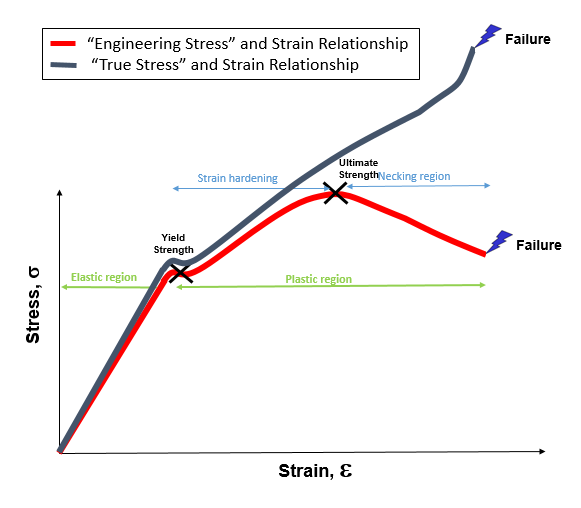
Fundamentals of metals, Solidification, Phase transformations and phase diagrams, Microsegregation, Basic principles of heat treatment, Spinodal decomposition, Plastic deformation, Corrosion and oxidation, Metal properties and tests, Tensile test and StressStrain Diagram, Metallographic examination, Extractive metallurgy, Steel makingIntial length 50mm ,intial area mm^2 ,calculate elongation ,stress ,stress and draw curve in excelThe ultimate strength is completely obscured in a true stressstrain curve However, the engineering stressstrain curve hides the true effect of strain hardening The true stressstrain curve is ideal for showing the actual strain (and strength) of the material


Solved A Using The 0 2 Strain 0 002 Strain Offset Met Chegg Com


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd
Yield stress and strength will now be sought Yield Stress Definition Consider a typical, ductile material stress strain curve as shown in Fig 1 Fig 1 Stress strain curve The related constitutive form will be taken to be that of the strain hardening type and applicable to any standard test such as those forAs the stress increases, the strain caused by it varies according to the properties of a material The relationship can be limned by a graph, and this graph is referred to as the stressstrain curve, where stress is plotted on the Yaxis and strain is plotted on the XaxisYoung's modulus with that yield strain as the xintercept, and locating the point where this line intersected the stressstrain curve The values for yield stress and yield strain were used along with Eqn 5 to calculate values for U el max, the material's maximum capacity to elastically absorb energy



A Normal Stress Strain Curve For Copper Showing The Yield Stress That Download Scientific Diagram



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
High mechanical strength and rigidity, without the need for fillers/reinforcements or other modifications Outstanding creep resistance and longterm fatigue endurance These features of high mechanical strength and toughness can be seen in this overlay of stressstrain curves of high viscosity Delrin ® acetal homopolymers and standard acetalStress Stress is the ratio of applied force F to a cross section areadefined as "force per unit area" tensile stress stress that tends to stretch or lengthen the material acts normal to the stressed area;



Loading And Unloading Stress Strain Curve In Uniaxial Tension S Y Is Download Scientific Diagram


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



What Is The Difference Between True Stress Strain And Engineering Stress Strain Diagram Quora



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article



Motion Design 101 Stress Strain Curves Machine Design


Indian Institute Of Technology



Stress Strain Curve Diagram Basic Mechstudies



Figure Shows The Strain Stress Curve For A Given Material What Are A Young S Modulus And B Approximate Yield Strength For This Material
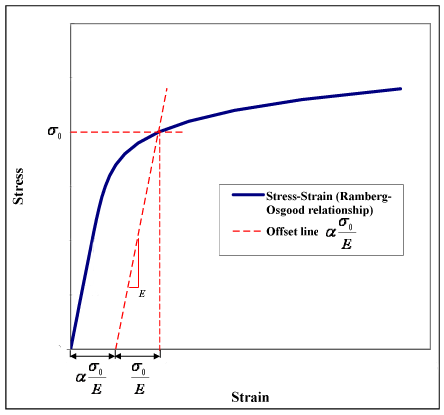


Ramberg Osgood Relationship Wikipedia


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables
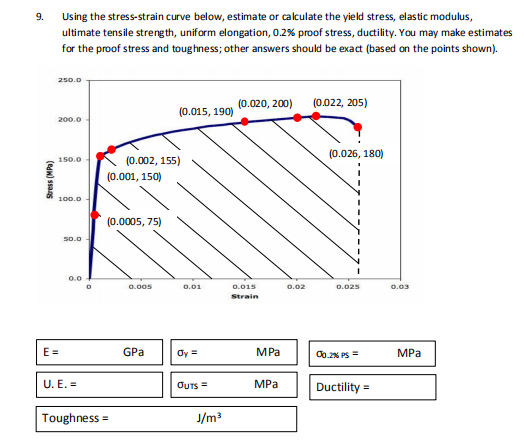


Solved Using The Stress Strain Curve Below Estimate Or C Chegg Com
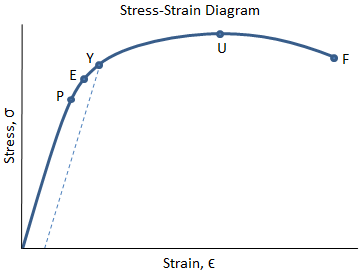


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange
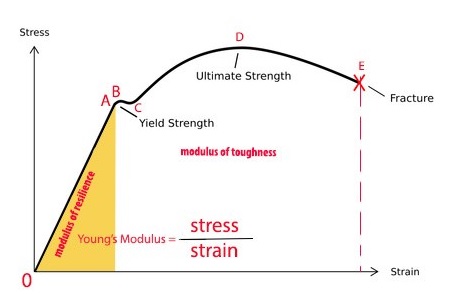


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



Chapter 26 Biomechanics Musculoskeletal Key
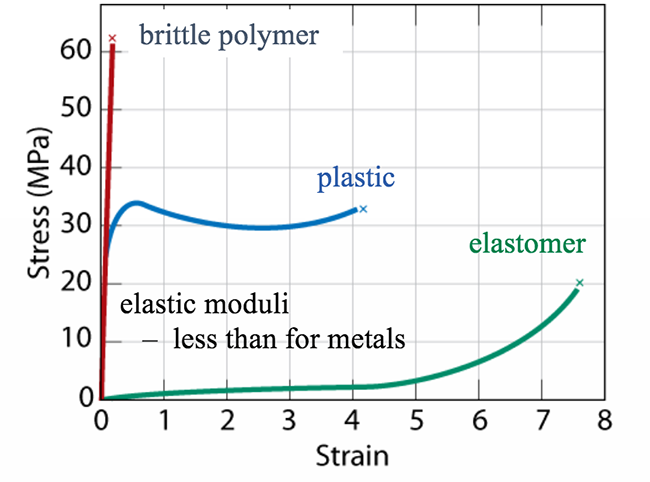


Mechanical Behavior Of Polymers Matse 81 Materials In Today S World



The Stress Strain Curve Obtained By Loading A Sample Of Compact Bone In Download Scientific Diagram


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Stress Strain Curve Strength Of Materials Smlease Design



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia
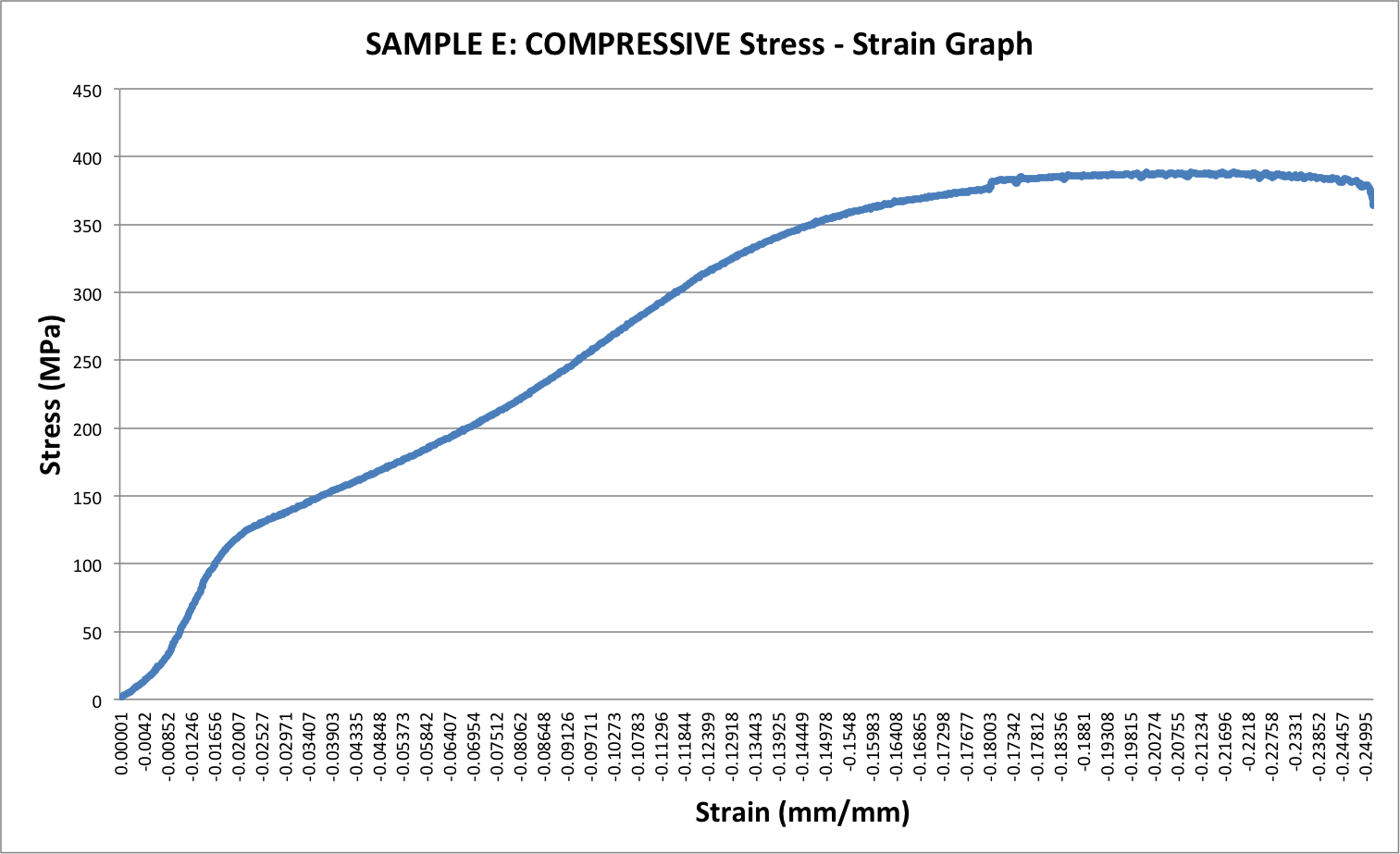


Solved Using The Compressive Stress Strain Curve Below D Chegg Com



A Engineering Compressive Stress Strain Curves B Yield Strength C Download Scientific Diagram



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing



Lecture Notes



Getting Started With Abaqus Explicit Keywords Version V6 6



Stress Strain Properties 2 Matlab Cody Matlab Central



Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
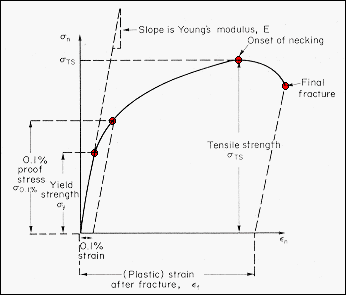


Materials
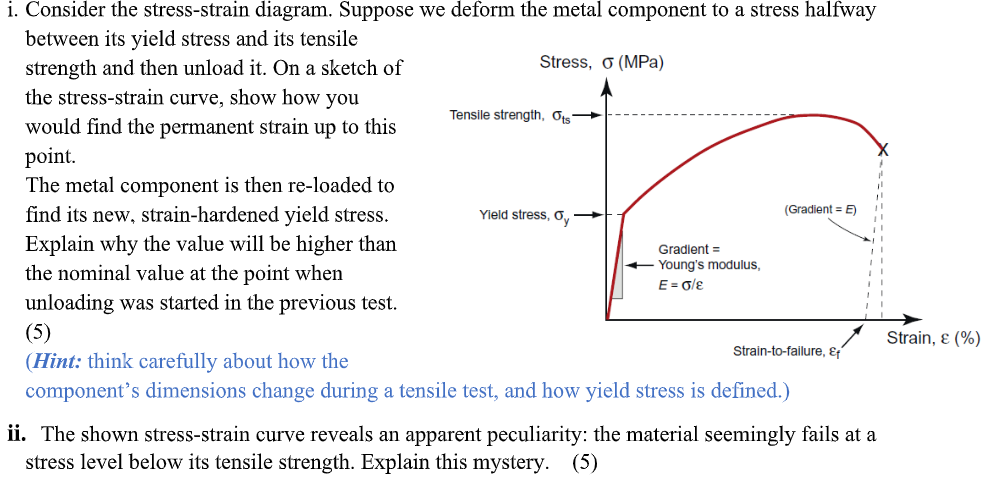


Solved I Consider The Stress Strain Diagram Suppose We Chegg Com



Stress Strain Curve Definition Examples Diagrams
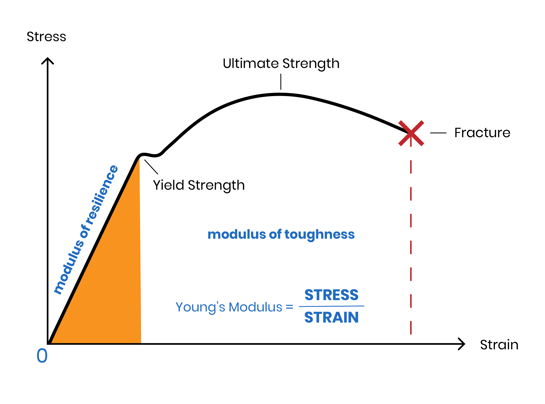


What Is Young S Modulus



Virtual Labs
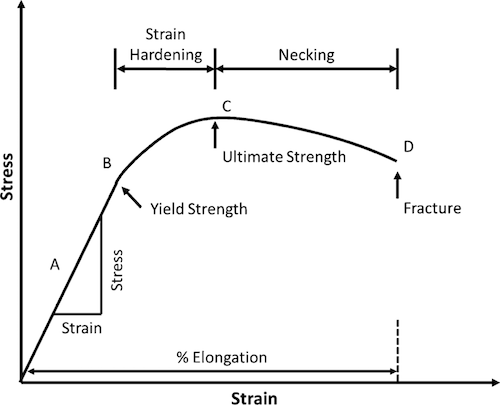


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness



What Changes A Stress Strain Curve Physics Stack Exchange



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



What Is Stress Strain Curve Mechanical Engineering Full Explanation



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
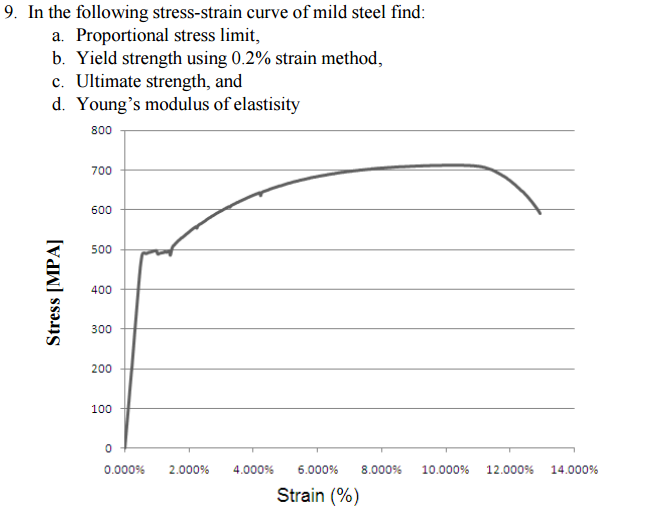


Solved In The Following Stress Strain Curve Of Mild Steel Chegg Com


Why Do We Use 0 2 Offset In Aluminum Stress Strain Curve Quora
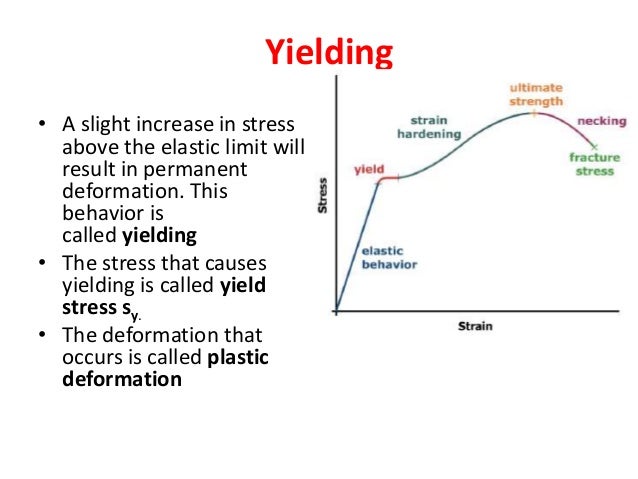


Stress Strain Curve



Stress Strain Curve For Steel Bars Figure 6 Represents Bilinear Download Scientific Diagram



Strength At Break Tensile
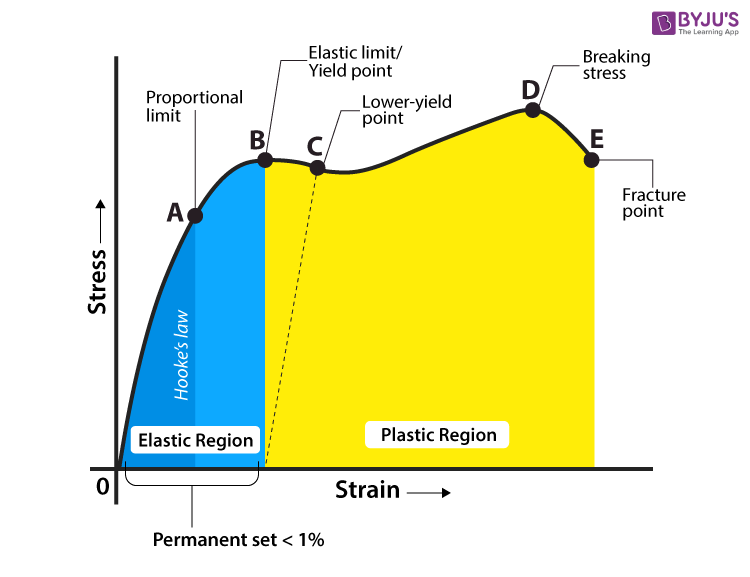


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau


Q Tbn And9gcry5eg9vw0pulzgan6nm7ceakmw8q02uis6m 0h78lr4trsyvo1 Usqp Cau



Stress Strain



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Stress Strain Behavior Of Polymers
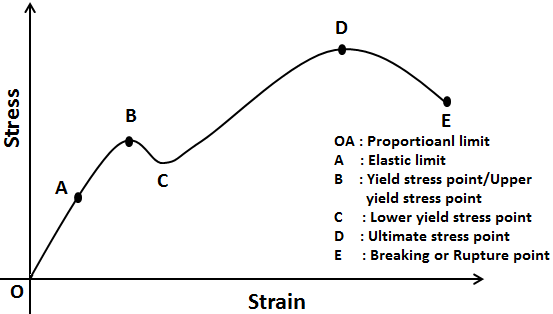


Stress Strain Curve Myrank



Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Explained Civilmint



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
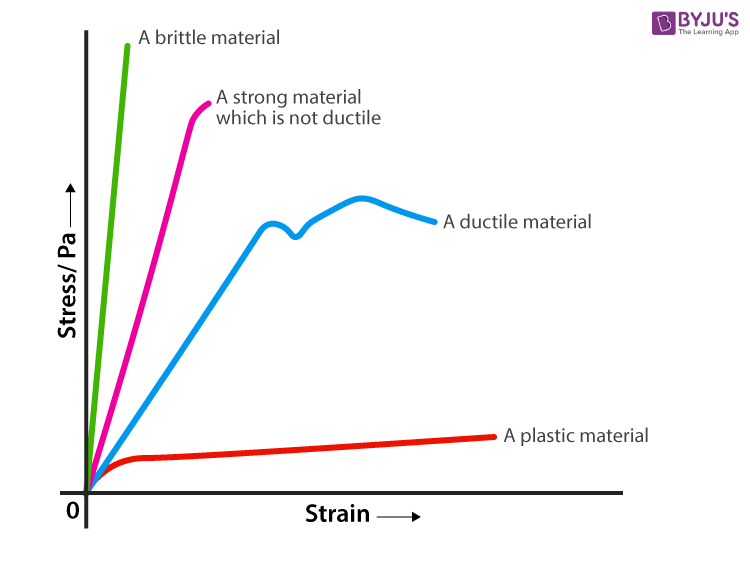


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
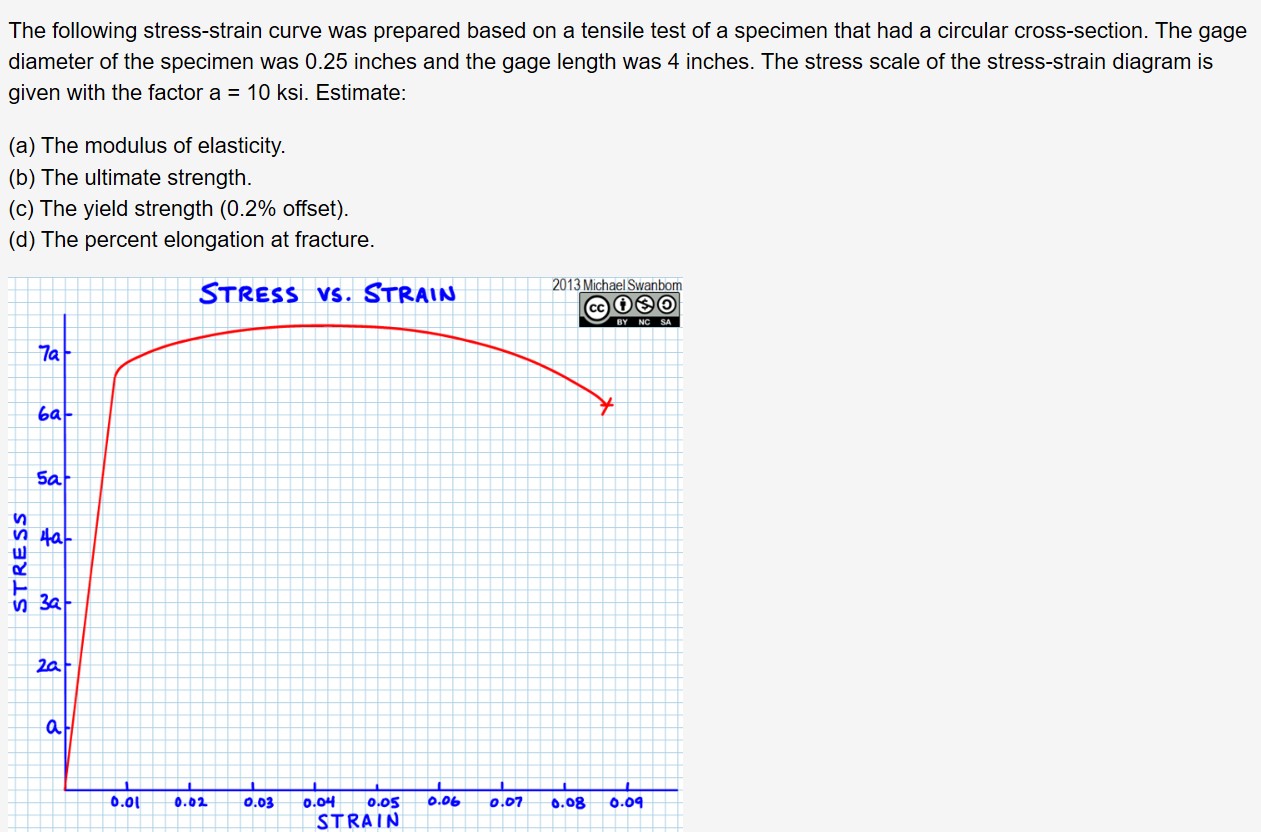


Answered The Following Stress Strain Curve Was Bartleby



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Stress Strain Curve Full Explanation Mech4study



What Changes A Stress Strain Curve Physics Stack Exchange


Q Tbn And9gcqdhkmo7hherjjmwerev9j1zxqfwpmjetj5gvnkildcbtyau41x Usqp Cau



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



The Stress Strain Curve Obtained By Loading A Sample Of Compact Bone In Download Scientific Diagram



What Is The Yield Point In A Stress Strain Diagram Quora
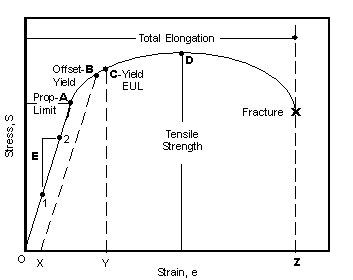


Astm E8 Measuring The Tensile Strength Of Metals
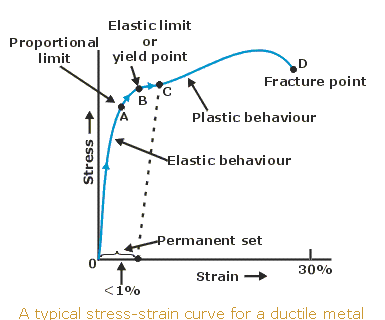


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Analysis Videos And Examples


Resiliency And Toughness Matse 81 Materials In Today S World


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


コメント
コメントを投稿